Stay prepared for what’s next in Hunter syndrome
There are new scientific advancements on the horizon with the goal of addressing critical unmet needs for patients with Hunter syndrome.7-10
Sign up to stay informedWhy GAG normalization in the brain matters for all patients with Hunter syndrome11-13
While severe Hunter syndrome is characterized by GAG accumulation in the brain and neurocognitive decline, patients with attenuated Hunter syndrome may also experience behavioral issues, inattentiveness, and hyperactivity.11-13
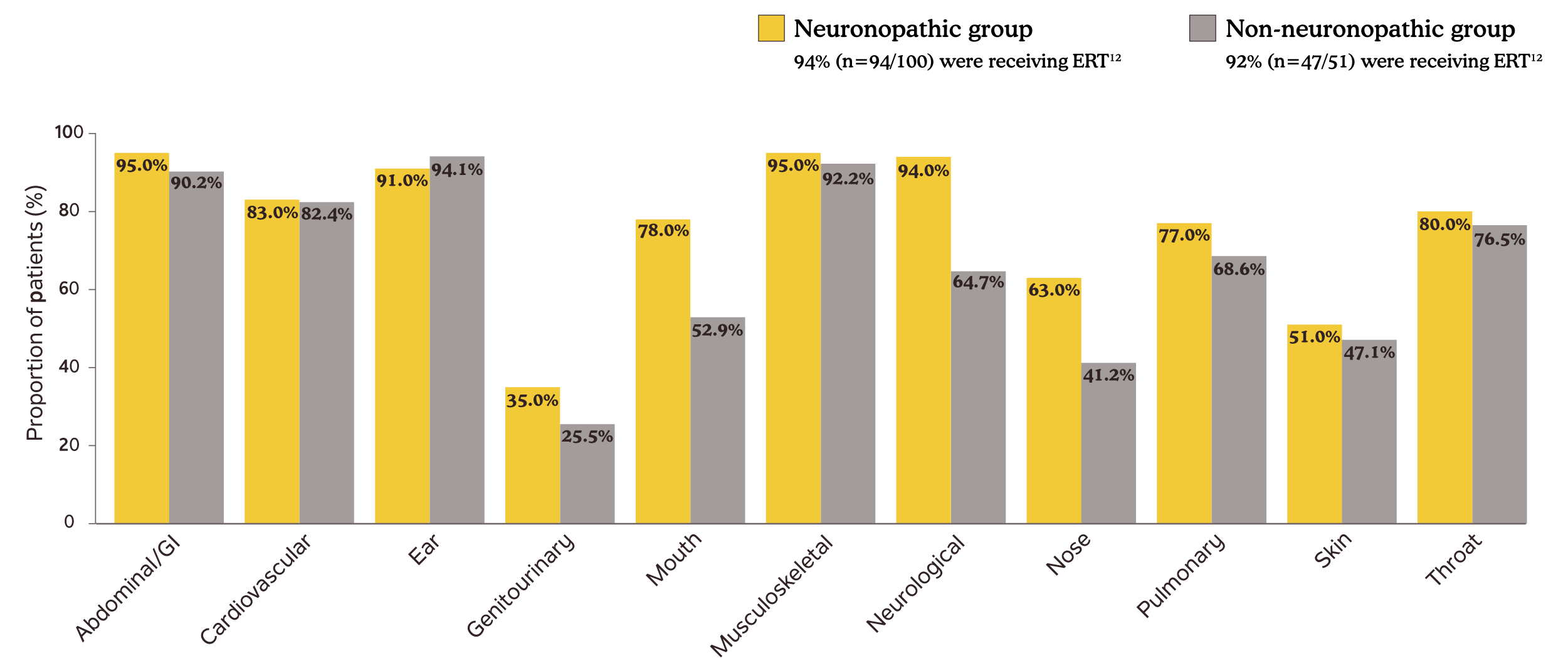
GAG levels are elevated in the brain of patients with severe or attenuated Hunter syndrome11
CSF GAG level (ng/mL)
Children without Hunter syndrome (n=201)
<37-202
Adults without Hunter syndrome (n=31)
<37-95
Children with attenuated Hunter syndrome (n=2)
357-373
Adults with attenuated Hunter syndrome (n=4)
382-1181
Children with severe Hunter syndrome (n=19)
424-3427
Data based on an analysis from 4 studies of GAG levels in the CSF in 257 individuals, including 25 with Hunter syndrome. These 4 studies included a phase 1-2, multicenter, randomized, open-label, interventional study of Hunter syndrome patients with cognitive manifestations; a multicenter study of pediatric and adult Hunter syndrome patients; a single-center study of healthy adult volunteers; and analysis of samples from children without Hunter syndrome.11
In a study that included 51 patients with non-neuronopathic Hunter syndrome, 65% (n=33/51) reported neurologic symptoms by age 10 and 33% (n=17/51) after age 10.12,a
aClinical manifestations classified in this study were recorded using predefined fields from the HOS database.12
CSF=cerebrospinal fluid; GAG=glycosaminoglycan; HOS=Hunter Outcome Survey.
GAG accumulation continues in the brain and body due to insufficient clearance2,3,6
Despite current treatment, prolonged exposure to elevated GAG levels can contribute to a range of multisystem symptoms that worsen over time.12,14,15
- Both severe and attenuated Hunter syndrome patients experience varying degrees of somatic manifestations. Incomplete GAG reduction over time can contribute to joint pain, hearing loss, carpal tunnel syndrome, and—most importantly—respiratory and cardiac issues, which have been shown to be the primary cause of mortality16-22
- For many patients across the disease spectrum, neurologic issues such as cognitive decline and behavioral challenges emerge as part of the disease’s manifestations12
The impact of GAG accumulation should be considered for all patients. Individuals across the disease spectrum eventually develop clinically significant symptoms.12,22
Incomplete GAG reduction contributes to the continued development of disease manifestations12
Somatic and neurologic manifestations in patients in the Hunter Outcome Survey12,b
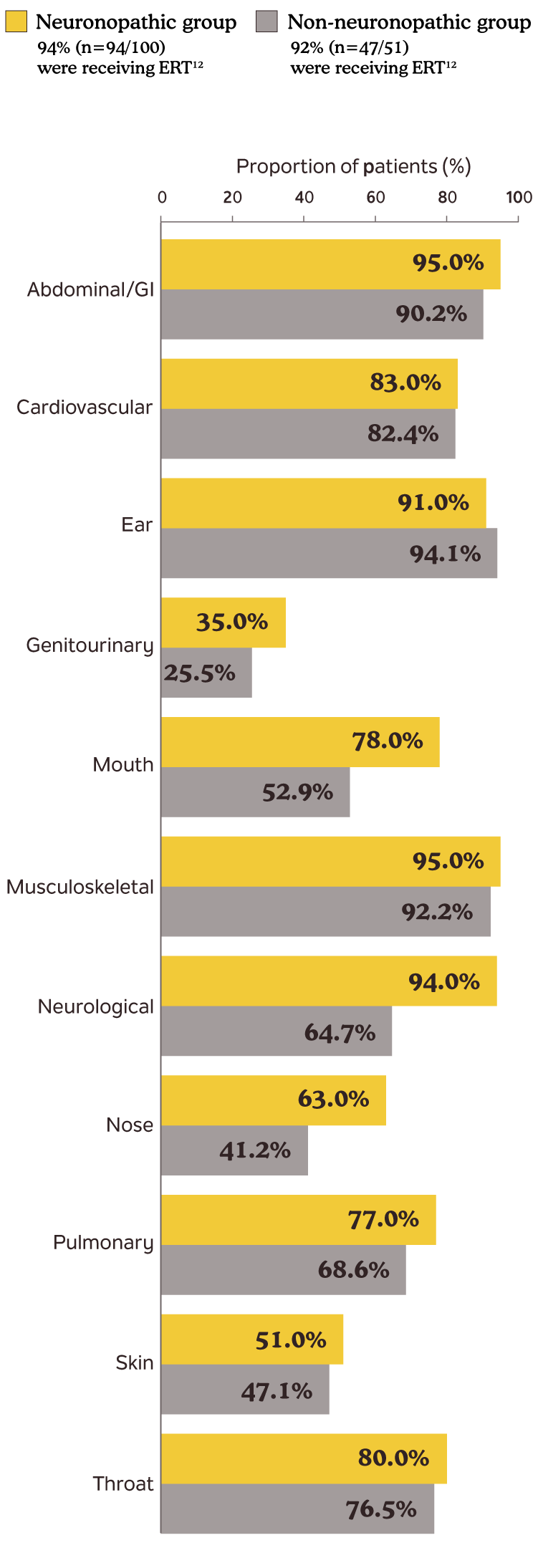
bData presented are disease manifestations in Hunter syndrome patients by age 10.12
Adapted from Lau H, Harmatz P, Botha J, Audi J, Link B. Clinical characteristics and somatic burden of patients with mucopolysaccharidosis II with or without neurological involvement: an analysis from the Hunter Outcome Survey. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2023;37:101005. © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc.
ERT=enzyme replacement therapy; GAG=glycosaminoglycan; GI=gastrointestinal.
Emerging biomarkers may provide additional promising information6,23-26
There are existing and emerging biomarkers analyzed from urine, blood, and CSF that can provide information to help with disease management.6,23-26
Key CNS biomarkers that may help in disease assessment8-10
The use of CNS biomarkers in Hunter syndrome continues to evolve and may have utility in the future to support disease management.6
In Hunter syndrome, heparan sulfate (HS) is one major GAG that accumulates in the brain.6,27
Measurement of CSF HS can reflect GAG accumulation in the brain, but clinical utility may be limited due to the invasiveness of sample collection.25
NfL is a protein that serves as a structural component of neurons in the brain, and it is released into the bloodstream in the event of neuronal degeneration or damage and has been correlated with cognitive decline in other neurodegenerative conditions.28-32,c
Serum NfL provides a less invasive alternative for monitoring neurodegeneration, with studies showing a correlation between elevated NfL levels and CSF HS concentrations.6,33
cHuntington's disease and Parkinson's disease.30,32
The critical role of monitoring somatic GAG burden34
Regular monitoring of uGAGs helps assess treatment response and offers early warning signs of disease progression.26,35
In a retrospective study, sustained reductions in uGAG levels correlated with improved walking distance and growth, highlighting the value of uGAG monitoring in treatment evaluations.36,d
Clinicians also noted greater improvements in global impressions of change, measured on the 7-point CGI-C scale, among patients with uGAG reductions of 50% or more vs those with smaller reductions.36,d
dBased on a retrospective study that included 18 patients with MPS I, 23 with MPS II, and 9 with MPS VI, who had been treated with ERT for at least 1 year.36
Key CNS biomarkers that may help in disease assessment8-10
The use of CNS biomarkers in Hunter syndrome continues to evolve and may have utility in the future to support disease management.6
In Hunter syndrome, heparan sulfate (HS) is one major GAG that accumulates in the brain.6,27
Measurement of CSF HS can reflect GAG accumulation in the brain, but clinical utility may be limited due to the invasiveness of sample collection.25
NfL is a protein that serves as a structural component of neurons in the brain, and it is released into the bloodstream in the event of neuronal degeneration or damage and has been correlated with cognitive decline in other neurodegenerative conditions.28-32,c
Serum NfL provides a less invasive alternative for monitoring neurodegeneration, with studies showing a correlation between elevated NfL levels and CSF HS concentrations.6,33
cHuntington's disease and Parkinson's disease.30,32
CGI-C=Clinician Global Impression of Change; CNS=central nervous system; CSF=cerebrospinal fluid; ERT=enzyme replacement therapy; GAG=glycosaminoglycan; MPS=mucopolysaccharidosis; NfL=neurofilament light; uGAG=urinary glycosaminoglycan.
Guiding future treatment decisions as science evolves
There are investigational treatments in development that are designed to cross the BBB.7-10,37,38 As the science advances, management of Hunter syndrome will continue to evolve.
By addressing both neuronopathic and somatic manifestations, future therapies hope to offer alternative options that better meet the needs of patients.7-10,37,38
Biomarkers like uGAGs provide a method to monitor disease. Tracking these levels over time may help inform ongoing disease management.26,35
Achieving GAG levels similar to those in people without Hunter syndrome has the potential to deliver clinical outcomes.6,20,36
BBB=blood-brain barrier; GAG=glycosaminoglycan; uGAG=urinary glycosaminoglycan.
Sign up to stay prepared for the latest advancements in Hunter syndrome

Community resources for Hunter syndrome
There are many helpful organizations for your patients and their caregivers that provide resources, build community, and increase awareness of Hunter syndrome.

Project Alive

National MPS Society

National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD®)
Download reference materials for your practice

Hunter syndrome HCP brochure
A guide for US healthcare professionals about the importance of monitoring and understanding GAG accumulation in patients with Hunter syndrome
DownloadGAG=glycosaminoglycan.